Kriging is a method often used in geostatistical science, and is called a Gaussian process in the popular field of machine learning.
Kriging is one of the spatial interpolation methods originally proposed by D.G. Krige. It is a method for spatial interpolation that uses the spatial correlation structure that data from observation points that are close in distance have a large similarity.
Algorithm is to interpolate between measured data point via unbiased minimum variance estimation, as described in Wikipedia .
Below code shows dimple implementation of ordinary kriging regression and with application for 1D time series data fitting using gauss variogram function.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def Test_Okriging ( x,Obsp,xx,nget,sill,rnge ) :
A = np. ones (( nobs+ 1 ,nobs+ 1 )) # +1 for lagrange multiplier
Cd = np. ones (( nobs+ 1 ,nobs+ 1 ))
b [ nobs ] = 1 # 1 = lagrange multiple
# Variogram_Generation(Cd,A,Obsp,pos,nget,sill,rnge)
#------------------------------------------------
# Covariance Generation by Data-Data Distance
for j in range ( i, nobs ) :
Cd [ i ][ j ] = np.linalg. norm ( x [ i ] -x [ j ])
#------------------------------------------------
# Variogram: Spherical/Gaussian Method
for j in range ( i, nobs ) :
A [ i ][ j ] = A [ j ][ i ] = nget + sill*np. exp ( -3 *Cd [ i ][ j ] ** 2 / ( rnge** 2 ))
#---------initialize values--------
vvval = np. ones (( int ( len ( xx ))))
distance = np.linalg. norm ( xx [ i ] -x [ k ])
b [ k ] = nget + sill*np. exp ( -3 *distance** 2 / ( rnge** 2 ))
OKest = np. sum ([ Weit [ j ] *Obsp [ j ] for j in range ( 0 , nobs )])
#--------- Return! ---------
#------------------------------------------
#------------------------------------------
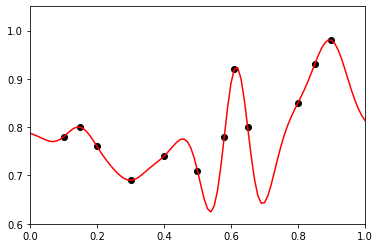
X = np. array ([ 0.10 , 0.15 , 0.20 , 0.30 , 0.40 , 0.50 , 0.58 , 0.61 , 0.65 , 0.80 , 0.85 , 0.90 ])
Y = np. array ([ 0.78 , 0.80 , 0.76 , 0.69 , 0.74 , 0.71 , 0.78 , 0.92 , 0.80 , 0.85 , 0.93 , 0.98 ])
pred_X = np. arange ( 0 , 1.1 , 0.01 )
#------------------------------------------
# Ordinary Kriging Estimation
#------------------------------------------
pred_Y = Test_Okriging ( X,Y,pred_X, 0.0 , 0.1 , 0.12 )
plt. plot ( pred_X, pred_Y, color = 'red' )
plt. xlim ( 0.0 , 1.0 ) ; plt. ylim ( 0.6 , 1.05 )
#%%
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import linalg
def Test_Okriging(x,Obsp,xx,nget,sill,rnge):
nobs = len(Obsp)
A = np.ones((nobs+1,nobs+1)) # +1 for lagrange multiplier
b = np.ones((nobs+1,1))
Cd = np.ones((nobs+1,nobs+1))
b[nobs]= 1 # 1 = lagrange multiple
# Variogram_Generation(Cd,A,Obsp,pos,nget,sill,rnge)
#------------------------------------------------
# Covariance Generation by Data-Data Distance
for i in range(nobs):
for j in range(i, nobs) :
Cd[i][j] = np.linalg.norm(x[i]-x[j])
#------------------------------------------------
# Variogram: Spherical/Gaussian Method
for i in range(nobs) :
for j in range(i, nobs) :
A[i][j] = A[j][i] = nget + sill*np.exp(-3*Cd[i][j]**2/(rnge**2))
#---------initialize values--------
vvval = np.ones((int(len(xx))))
for i in range(len(xx)):
for k in range(nobs) :
distance = np.linalg.norm(xx[i]-x[k])
b[k] = nget + sill*np.exp(-3*distance**2/(rnge**2))
Weit = linalg.solve(A,b)
OKest = np.sum([Weit[j]*Obsp[j] for j in range(0, nobs)])
vvval[i] = OKest
#--------- Return! ---------
return vvval
#------------------------------------------
# Observed Data
#------------------------------------------
X = np.array([0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.58, 0.61, 0.65, 0.80, 0.85, 0.90])
Y = np.array([0.78, 0.80, 0.76, 0.69, 0.74, 0.71, 0.78, 0.92, 0.80, 0.85, 0.93, 0.98])
pred_X = np.arange(0, 1.1, 0.01)
#------------------------------------------
# Ordinary Kriging Estimation
#------------------------------------------
pred_Y = Test_Okriging(X,Y,pred_X,0.0,0.1,0.12)
plt.plot(X, Y, 'ko')
plt.plot(pred_X, pred_Y, color = 'red')
plt.xlim(0.0, 1.0); plt.ylim(0.6, 1.05)
plt.show()
# %%
#%%
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import linalg
def Test_Okriging(x,Obsp,xx,nget,sill,rnge):
nobs = len(Obsp)
A = np.ones((nobs+1,nobs+1)) # +1 for lagrange multiplier
b = np.ones((nobs+1,1))
Cd = np.ones((nobs+1,nobs+1))
b[nobs]= 1 # 1 = lagrange multiple
# Variogram_Generation(Cd,A,Obsp,pos,nget,sill,rnge)
#------------------------------------------------
# Covariance Generation by Data-Data Distance
for i in range(nobs):
for j in range(i, nobs) :
Cd[i][j] = np.linalg.norm(x[i]-x[j])
#------------------------------------------------
# Variogram: Spherical/Gaussian Method
for i in range(nobs) :
for j in range(i, nobs) :
A[i][j] = A[j][i] = nget + sill*np.exp(-3*Cd[i][j]**2/(rnge**2))
#---------initialize values--------
vvval = np.ones((int(len(xx))))
for i in range(len(xx)):
for k in range(nobs) :
distance = np.linalg.norm(xx[i]-x[k])
b[k] = nget + sill*np.exp(-3*distance**2/(rnge**2))
Weit = linalg.solve(A,b)
OKest = np.sum([Weit[j]*Obsp[j] for j in range(0, nobs)])
vvval[i] = OKest
#--------- Return! ---------
return vvval
#------------------------------------------
# Observed Data
#------------------------------------------
X = np.array([0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.58, 0.61, 0.65, 0.80, 0.85, 0.90])
Y = np.array([0.78, 0.80, 0.76, 0.69, 0.74, 0.71, 0.78, 0.92, 0.80, 0.85, 0.93, 0.98])
pred_X = np.arange(0, 1.1, 0.01)
#------------------------------------------
# Ordinary Kriging Estimation
#------------------------------------------
pred_Y = Test_Okriging(X,Y,pred_X,0.0,0.1,0.12)
plt.plot(X, Y, 'ko')
plt.plot(pred_X, pred_Y, color = 'red')
plt.xlim(0.0, 1.0); plt.ylim(0.6, 1.05)
plt.show()
# %%
1D ordinary kriging